Is the inorganic compound BCl3 polar or nonpolar? If shapes are the basis of polarity, then BCl3 is a polar molecule. But if you base it on BCL3’s electronegativity, then it is nonpolar.
Which answer is correct?
Let us see the shape, geometry, and all other factors about Boron Trichloride to determine its polarity or non-polarity.
Table of Contents
Polarity or Nonpolarity of Boron Trichloride
The structure of Boron Trichloride is Trigonal Planar which forms a T and is symmetrically arranged, revealing its non-polarity.
This centrally located boron has valence electrons, responsible for balancing the three chlorines causing it to be a part of a perfectly balanced trigonal pyramidal shape (1).
The contradiction is with the B-Cl bond, which shows polarity mainly because of the electronegativity difference of Boron 2.04) and Chlorine(3.16), and all three such bonds lie at 120 degrees to each other.
BCl3 is a planar molecular compound in which the three B – Cl molecular bonds are inclined at a bond angle of 120 degrees.
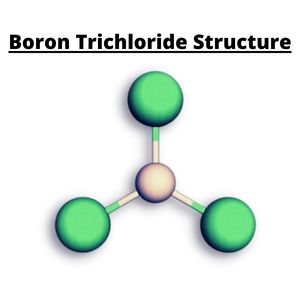
Molecular Geometry & Bond Angle
The chlorine halides are spaced symmetrically around the central boron atom. The three chlorine atoms have a negative charge, and the central atom boron in the center has a positive charge.
Though BCl3 does not fully complete its octet, based on the ruling of Lewis Structure, even with lone pairs, it can still come up with a nonpolar molecule. It has three chlorides bonded and no lone pair making the molecular geometry trigonal planar.
Since we have the same pull in these organic compounds and no electrical dipole formed, there is no dipole moment. An important factor in helping determine a compound’s nature is its symmetrical geometry, such as carbon disulfide (CS2).
Factors That Determine Polarity

Shape
The shape after the same amount of molecules attached will become the basis, whether this is nonpolar or not. If the arrows have the same length and have a symmetrical structure, then this is nonpolar. The bond angle seen at the lewis structure will help determine the shape.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a measure of the capability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons. Electronegativity is a periodic property affecting valence electrons. The charge distribution of different atoms attached will determine the polarity or non-polarity of the molecule.
Dipole Moment
There is a separation of positive and negative charges because of the unequal attraction for the bonded valence electrons. B, boron in the periodic table, and Cl have different values in terms of electronegativities.
Hence chlorine (E.N. = 3.00) is more electronegative than the Boron (E.N. = 2.00).
As a result, the B–Cl bond forms polar bonds and carries a finite zero dipole moment.
Related Posts:
If BCl3 is a Non-polar Molecule, Why Does It Form Polar Bonds?
While it is true that BCl3 is non-polar, it forms bonds because the B-Cl bond itself is not non-polar, caused by the difference in electronegativity of Boron(2.04) and Chlorine(3.16).
All three valence electrons, B-Cl bonds that are at a distance of 120 degrees from each other, the chemical bond still cancels out, making the net dipole moment zero.
Why Does BCl3 Have Covalent Bonds?

Boron trichloride or BCl3 is a combination of two atoms boron and chlorine. B atoms and Cl atoms are both nonmetals making them covalent compounds.
As B electrons in BCl3 undergo sp2 hybridization, the resultant shape is trigonal planar. B and Cl form polar covalent bonds, but three other covalent bonds have the same bond moments. Thus the sum of three valence electrons comes out to be zero dipole moment in a single bond.
FAQS
Boron Trichloride is a reactive gas that can serve as rocket fuel as it produces hydrogen chloride. This is not an ordinary boron atom turned chemical compound because once it is on hydrolysis with water and other alcohols, this can form hydrogen chloride.
The material used to produce elemental boron comes from bonded atoms of BCl3. Fumes from the chemical compound BCl3 can easily irritate the eyes, along with the mucous membranes. It is corrosive to metals, tissues, and considered toxic in nature.
Another use for this colorless gas is a soldering flux for aluminum, tungsten, iron, zinc, and monel metal.
Based on the Lewis theory of Acid and base, acids are chemicals accepting pairs of electrons.
Because of the electron-deficient boron, the central atom of BCl3 allowed the molecule to accept an extra pair of electrons and, hence, acts as a Lewis Acid. At room temperature, this is a colorless gas that forms fumes and has a pungent odor. Its melting point is −107.3 °C or −161.1 °F, and the boiling point of boric acid is around 12.6 °C or 54.7 °F. This is soluble in compounds like CCl4, ethanol.
So, Is BCl3 Polar or Nonpolar?
BCl3 is a nonpolar molecule. To have a polar bond, it needs to have an asymmetrical shapeshift in electron density to form an electrical dipole, but this is not the case for BCl3.
BCl3 is a chemical compound with an SP2 hybridization type. In BCl3, Boron as a central atom consists of three bonded chlorine atoms with no lone pair of electrons left. Also, symmetrical molecular geometry is an important factor in determining the nonpolar nature of a compound.
The electronegativity difference also contributed to the non-polarity of BCl3.
So, is BCl3 polar or nonpolar? A science enthusiast would say, yes, it is.
Thank you for reading this far! I hope that the information provided in this article will be helpful to you.
Reference:
- http://www.csun.edu/~hcchm001/shapes-polarity.pdf